

News
 电商部
电商部  2025-09-09 18:34:30
2025-09-09 18:34:30 Comparison of Performance and Technological Innovations between Solid State Drives 2.0 and 3.0
In today's rapidly changing data storage technology, solid-state drives (SSDs) have gradually become the preferred choice for many users to upgrade their computers due to their excellent performance and stability. In the development process of SSDs, the difference between 2.0 and 3.0 versions is particularly significant. They not only differ in transmission speed and interface standards, but also bring a qualitative leap in overall user experience.

Firstly, in terms of transmission speed, solid-state drive 3.0 has significantly improved compared to version 2.0. This is due to the optimization of its internal architecture and the upgrade of interface standards. Solid state drives 3.0 commonly use PCIe interfaces or more advanced M.2 interfaces, which support higher data transfer rates. In contrast, solid-state drives 2.0 mostly use SATA interfaces, and although their transfer speed was already quite impressive at the time, it still pales in comparison to the 3.0 version. In practical applications, this means that computers using solid-state drives 3.0 can enjoy faster response times and higher work efficiency when starting up, loading applications, and processing large files.

Secondly, the difference in interface standards is also an important difference between Solid State Drive 2.0 and 3.0. Solid state drive 3.0 supports advanced transfer protocols such as NVMe, which have significant advantages in data transfer efficiency, delay control, and multitasking capabilities. Solid state drive 2.0 mainly relies on older transmission protocols such as AHCI. Although these protocols were sufficient to meet the needs of most users at that time, their performance bottlenecks gradually emerged when facing modern multitasking and high load scenarios.
In addition, solid-state drive 3.0 also has impressive performance in power consumption control, heat dissipation performance, and compatibility. With the continuous advancement of technology, solid-state drive 3.0 can effectively reduce power consumption and heat generation while maintaining high performance, thereby extending the service life of computers and improving overall stability. At the same time, Solid State Drive 3.0 also has better compatibility and can adapt to more types of computer motherboards and storage devices.
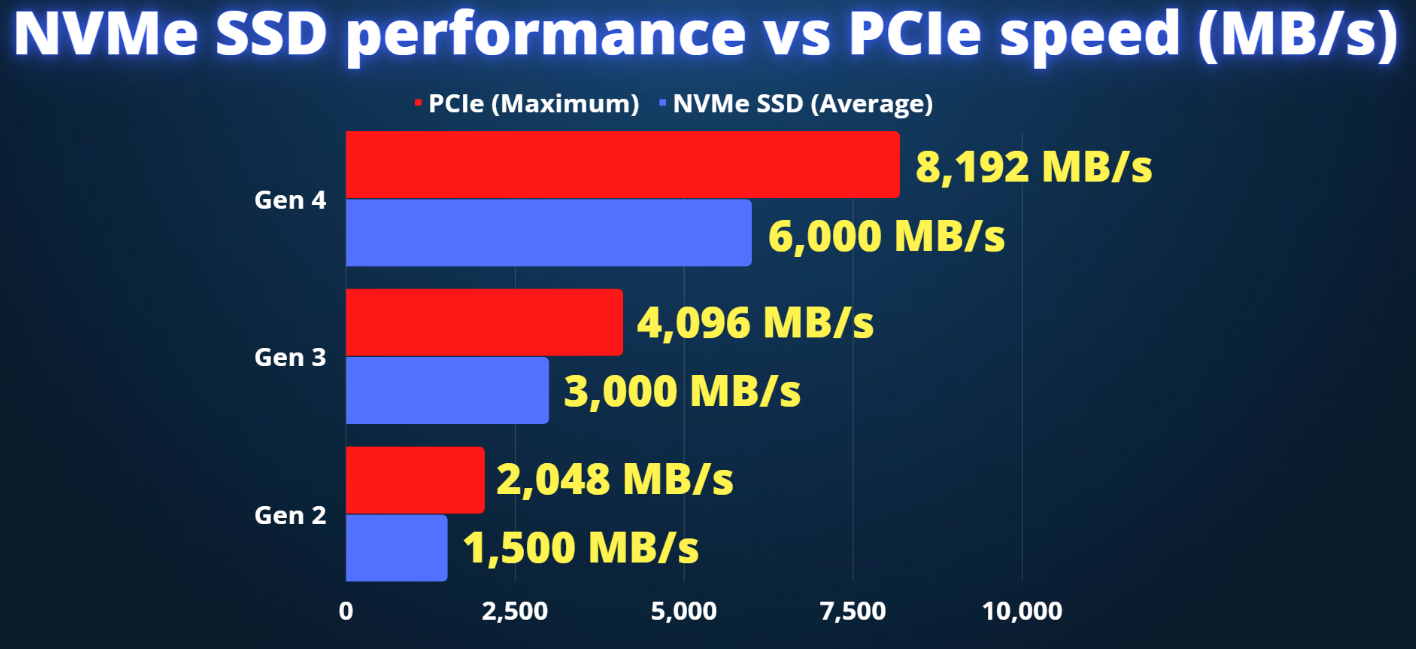
In summary, the differences between solid-state drives 2.0 and 3.0 are mainly reflected in various aspects such as transmission speed, interface standards, power consumption control, heat dissipation performance, and compatibility. With the continuous development of technology, solid-state drive 3.0 has become mainstream in the market, bringing users a smoother and more efficient data storage experience. For users who pursue ultimate performance and stability, choosing Solid State Drive 3.0 is undoubtedly a wise decision.



























































