

News
 电商部
电商部  2026-01-14 15:26:30
2026-01-14 15:26:30 How to Read Laptop Memory Module Labels: A Complete Guide
Laptop memory module labels contain a wealth of information that can be overwhelming for first-time buyers or upgraders. However, learning to decode these labels is crucial for ensuring compatibility and selecting the right module for your needs. A typical label includes details about capacity, generation, frequency, latency, module type, and voltage— all of which impact performance and compatibility with your laptop.
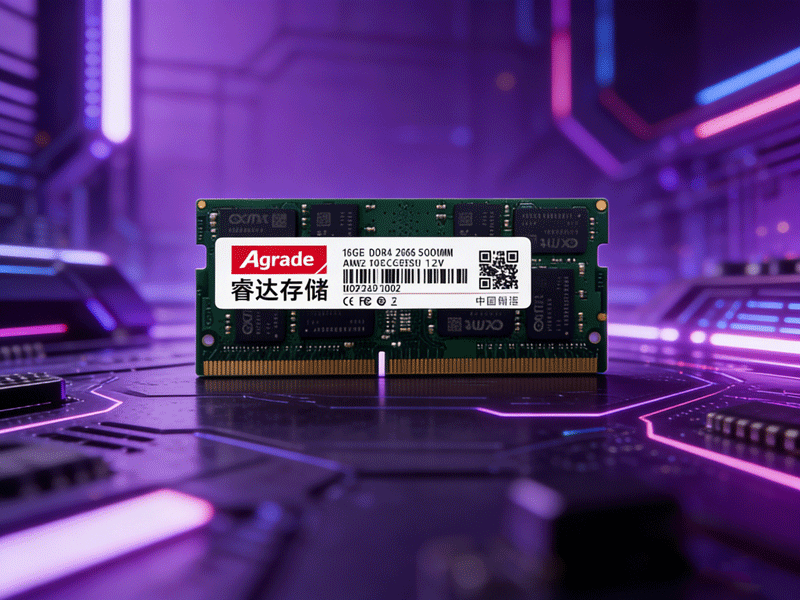
Let’s break down a sample label: “16GB 2Rx8 PC4-3200S-11-12-E3 SO-DIMM 1.2V”. The first part, “16GB”, indicates the module’s capacity, which is the amount of temporary data storage it can provide. Common capacities for laptop memory modules are 8GB, 16GB, and 32GB, with high-end workstations supporting up to 64GB per module. It’s important to note that some older laptops have a maximum memory capacity limit, so check your device’s specifications before purchasing a high-capacity module.
“2Rx8” refers to the module’s rank and chip density. “2R” means dual-rank, meaning the module has memory chips on both sides of the PCB (Printed Circuit Board), while “1R” indicates single-rank (chips on one side). Dual-rank modules generally offer better compatibility with older motherboards but may consume slightly more power. “x8” denotes the chip width (8 bits), which affects data transfer efficiency— x8 is the most common for consumer-grade laptop memory.
“PC4-3200S” identifies the generation and frequency. “PC4” corresponds to DDR4, with PC3 for DDR3 and PC5 for DDR5. The number “3200” represents the module’s effective frequency (3200MHz), and the “S” suffix indicates it’s a SO-DIMM (laptop-specific) module— desktop modules use “U” (Unbuffered) or no suffix. Frequency determines how quickly data can be read from and written to the module; higher frequencies result in faster performance, though this is limited by the laptop’s motherboard and processor.
“11-12” are the primary latency values: CL11 (CAS Latency) and tRCD (RAS to CAS Delay). Latency refers to the time it takes for the module to respond to a data request— lower values mean faster response times. Full latency specifications include four values (CL-tRCD-tRP-tRAS), but labels often abbreviate to the first two. Finally, “1.2V” indicates the operating voltage, confirming this is a standard DDR4 module (low-voltage DDR4L uses 1.05V). Matching the voltage to your laptop’s requirements is critical to avoid damage or instability.



























































